Writen by
Chai Biscuit
9:22 PM
-
0
Comments
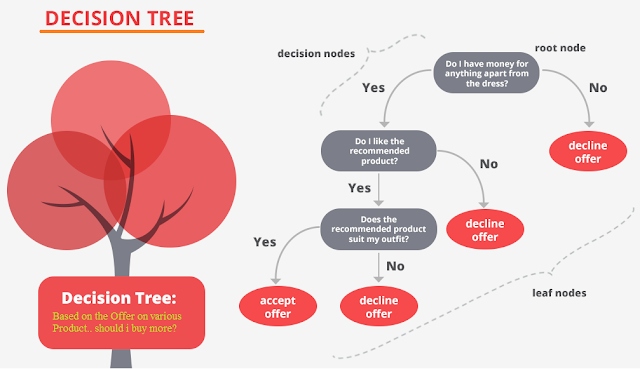 |
| Credit: Datascience Foundation |
Over fitting:
Over fitting is one of the most practical difficulty for decision tree models. This problem gets solved by setting constraints on model parameters and pruning (discussed in detailed below).
 |
| Credit: ROUCHI.AI |
Not fit for continuous variables:
While working with continuous numerical variables, decision tree looses information when it categorizes variables in different categories.
Cannot extrapolate:
Decision tree can’t extrapolate beyond the values of the training data. For example, for regression problems, the predictions generated by a decision tree are the average value of all the training data in a particular leaf.
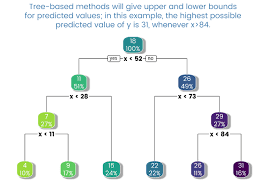 |
| Credit: Google |
Decision trees can be unstable:
Small variations in the data might result in a completely different tree being generated. This is called variance, which needs to be lowered by methods like bagging and boosting.
No Guarantee to return the globally optimal decision tree.
This can be mitigated by training multiple trees, where the features and samples are randomly sampled with replacement
💕









No comments
Post a Comment